Understanding Megapixels and Resolution: A Technical Perspective
When we talk about higher megapixel counts in sensors, our immediate thought is increased resolution—a concept partially true but with important nuances. In reality, what you gain with more pixels (for the same optics, scene size, and pixel pitch) is an expanded field of view.
Field of View vs. Resolution
Think of these two concepts as distinct yet related:
- Field of View refers to the angular width captured by your sensor under fixed conditions.
- Resolution, conversely, involves the number of pixels available per unit area in a scene.
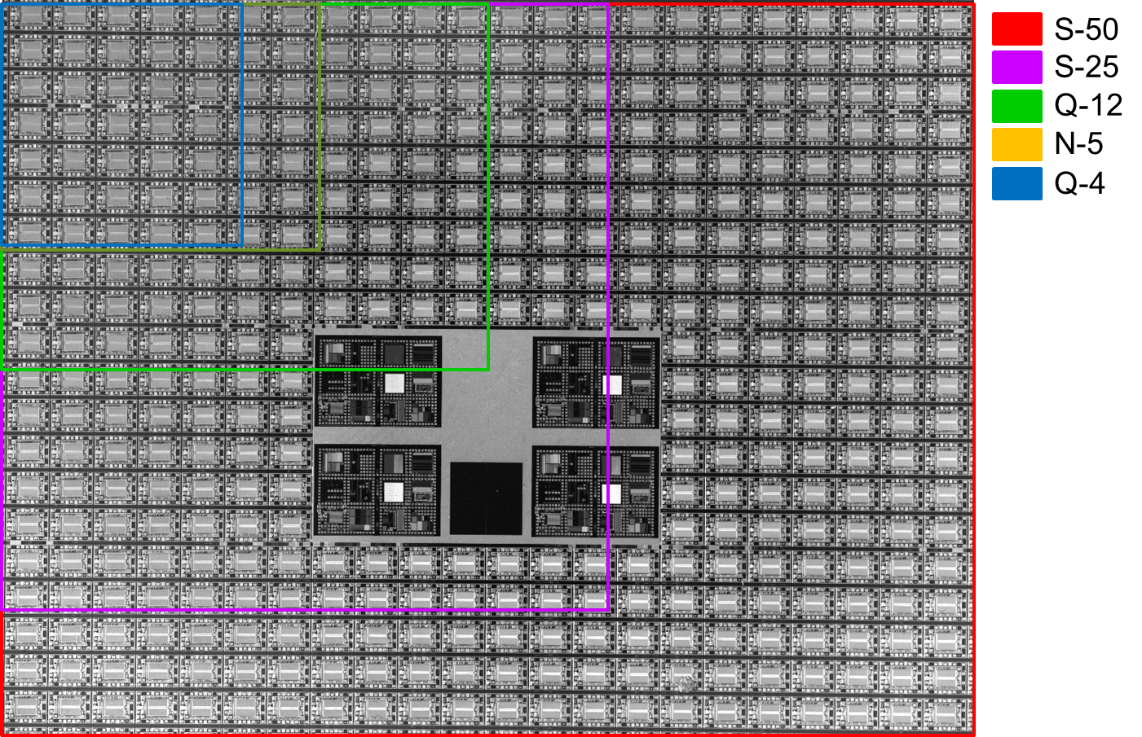
These principles are clearly demonstrated through several examples using Adimec cameras with varying megapixel counts (Q-4, N-5, Q-12, S-25, and S-50).
Demonstration 1: Semiconductor Wafer Imaging
When examining semiconductor wafers under fixed optical conditions:
graph TD
A[Low-Megapixel Camera] --> B(FOV Example)
C[High-Megapixel Camera] --> D(Larger FOV Displayed)
Demonstration 2: PCB Analysis
The relationship between resolution and field of view becomes especially apparent when examining printed circuit boards (PCBAs). Higher-resolution cameras capture larger areas, but crucially maintain the ability to zoom into minute details without degradation.
How Resolution Impacts Imaging
There are two primary methods for achieving higher spatial resolution:
- Optics Adjustment: By modifying lens systems, you can increase pixel density on target.
- Pixel Size Reduction: Using smaller pixels in cameras with identical optical formats increases total pixel count while maintaining the same field of view.
Both approaches enable deeper digital zooming capabilities—allowing macro-to-micro transitions without physical magnification lenses.
Practical Example
The following image demonstrates detail capture capability using a high-resolution sensor:
graph LR
E[Patterned Wafer] --> F(Digital Zoom Focus)
G[50-Megapixel Sensor] --> H(Extreme Detail Resolution)
In summary, higher megapixels directly impact resolution in two fundamental ways: they expand field of view under identical conditions and enable superior digital zooming capabilities.
Last Updated: 2025-09-04 21:14:46